Chapter 5
Evaluative UX research: Methods to validate and improve UX
How do you know if your UX design actually works? Evaluative research helps teams test, measure, and refine product usability before and after launch.

How do you know if your product actually works for users? You test it.
Evaluative UX research helps you assess designs, find usability issues, and improve the user experience with real data. It ensures your product meets user expectations before it goes live—saving time, money, and user frustration.
This chapter breaks down evaluative research key methods, like usability testing and A/B testing, plus real-world examples of how UX teams have refined products based on user feedback.
What is evaluative research?
Evaluative research is a research method used to test and assess (aka evaluate) a product, feature, or concept to determine its effectiveness, usability, and overall user experience. It helps teams identify what works well, what needs improvement, and how users interact with a product in real-world conditions.
Also known as evaluation research or program evaluation, this kind of research is typically introduced in the early phases of the UX design process to test existing or new solutions until the product becomes ‘final.’
With evaluative research, we’re making sure the value is there so that effort and resources aren’t wasted.
Nannearl LeKesia Brown
UX Researcher at Figma
Share
How does evaluative research compare to generative and formative research?
UX research happens at different stages of product development, and each type of research serves a purpose:
- Generative research helps identify user needs and opportunities before design begins
- Formative research tests and refines designs as they’re being developed
- Evaluative research assesses whether the final product meets user expectations and performs well
Here’s a quick overview of generative vs. formative vs. evaluative research:
Generative research | Formative research | Evaluative research | |
|---|---|---|---|
Purpose | Explore user needs, behaviors, and pain points to inspire new ideas | Test and refine early designs before launch | Assess product usability, effectiveness, and performance |
When to use | Early in the design process, before solutions exist | During the design process, while refining prototypes | Throughout the product lifecycle—before launch, post-launch, and during iterations |
Focus | Identifying problems and opportunities | Improving designs before development | Measuring how well a product meets user needs |
Methods | User interviews, ethnographic studies, focus groups, open card sorting | Wireframe testing, prototype testing, early usability studies | |
Example | Conducting interviews to understand how users track expenses before building a budgeting app | Testing a prototype of the budgeting app to refine its layout and navigation | Running an A/B test to compare two versions of the budgeting app’s checkout flow |
Why is evaluative research important?
Evaluative research is important because it helps you:
- Refine and improve UX: Evaluative research allows you to test a solution and collect valuable feedback to refine and improve the user experience. For example, you can A/B test the copy on your site to maximize engagement with users.
- Identify areas of improvement: Findings from evaluative research are key to assessing what works and what doesn't. You might run usability testing to observe how users navigate your website and identify pain points or areas of confusion.
- Align your ideas with users: Research should always be a part of the design and product development process. When you allow users to evaluate your product early and often, you'll know whether you're building the right solution for your audience.
- Get buy-in: The insights you get from evaluative research can demonstrate the effectiveness and impact of your project. Show this information to stakeholders to get buy-in for future projects.
Pro tip ✨
You can also evaluate competitor solutions, to understand what works well in the current market. Mithila Fox, Director of Product Research at Contentful says: “Even before you have your own mockups, you can start by testing competitors or similar products. There’s a lot we can learn from what is and isn't working about other products in the market.”
3 Types of evaluative research for UX design
There are three types of evaluative studies you can tap into: formative research, summative research, and outcome research.
TL;DR:
1️⃣ Run formative research to test and evaluate solutions during the design process
2️⃣ Conduct a summative evaluation at the end to evaluate the final product
3️⃣ Use outcome evaluations to understand the impact on user behavior and satisfaction
1. Formative evaluation research
Formative research is conducted early and often during the design process to test and improve a solution before arriving at the final design.
Running a formative evaluation allows you to test and identify issues in the solutions as you’re creating them, and improve them as you go based on user feedback.
2. Summative evaluation research
A summative evaluation helps understand how a design performs overall. It’s usually done at the end of the design process to evaluate its usability or detect overlooked issues.
You can also use a summative evaluation to benchmark your new solution against a prior one, or that of a competitor.
Although summative evaluations are often quantitative, they can also be part of qualitative research.
3. Outcome evaluation research
Outcome evaluation research assesses the effectiveness of a design by measuring the changes it brings about in specific user behaviors and satisfaction.
This type of evaluation focuses on the short-term and long-term impacts on users, such as improved task completion rates or increased user engagement. Outcome evaluations help understand the real-world effectiveness of a product design and support data-driven decisions for future improvements.
When to use evaluative vs. generative research methods?
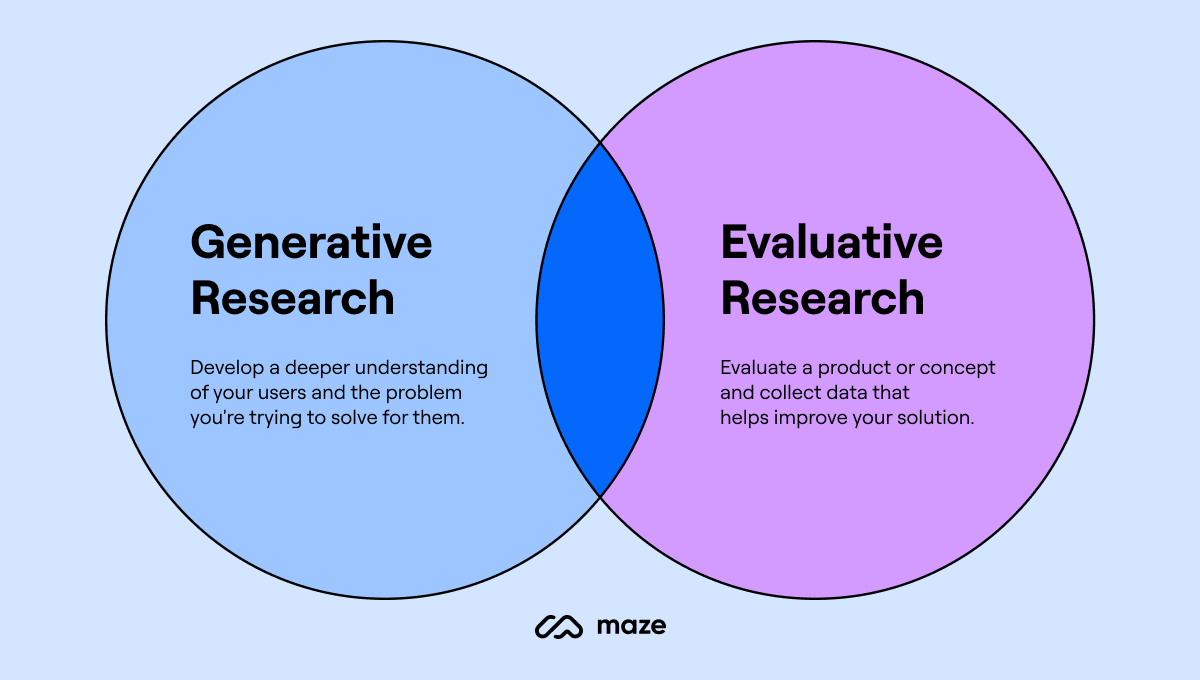
The difference between generative research and evaluative research lies in their focus:
- Evaluative research assesses and validates existing designs for improvements
- Generative methods investigate user needs for new solutions
Generative research helps us deeply understand our users and learn their needs, wants, and challenges. On the other hand, evaluative research helps us test whether the solutions we've come up with address those needs, wants, and challenges.
Mithila Fox
Director of Product Research at Contentful
Share
Generative and evaluative research are both valuable decision-making tools for researchers, and should both be used throughout the product development process to assess the product and get the evidence you need.
Evaluative research methods collect quantitative and qualitative user data through:
Generative research methods collect qualitative user data through:
Some research methods, such as UX surveys and user interviews, can be used in both generative and evaluative research, depending on the context and goals.
When creating your research plan, study the competitive landscape, target audience, needs of the people you’re building for, and any existing solutions. Depending on what you need to find out, you’ll be able to determine if you should run generative or evaluative research—or both.
Key methods in evaluative research (with examples)
“Evaluation research can start as soon as you understand your user’s needs,” says Mithila. Here are five typical UX research methods to include in your evaluation research process:

1. Surveys
User surveys can provide valuable quantitative and qualitative insights into user preferences, satisfaction levels, and attitudes toward a design or product. By gathering a large amount of data efficiently, surveys can identify trends, patterns, and user demographics to make informed decisions and prioritize design improvements.
There are many types of surveys to choose from, including:
- Customer satisfaction (CSAT) surveys: Measure users' satisfaction with a product or service through a straightforward rating scale, typically ranging from 1 to 5
- Net promoter score (NPS) surveys: Evaluate the likelihood of users recommending a product or service on a scale from 0 to 10, categorizing respondents as promoters, passives, or detractors
- Customer effort score (CES) surveys: Focus on the ease with which users can accomplish tasks or resolve issues, providing insights into the overall user experience
Some example questions for your next survey could include:
- How often do you use the product/feature?
- How satisfied are you with the product/feature?
- How often does the product/feature help you achieve your goals?
- How easy is the product/feature to use?
🚀 Want to supercharge your surveys to maximize insights?
Maze AI enables you to get more from your feedback surveys with AI-powered capabilities. From asking the Perfect Questions, to digging deeper with Dynamic Follow-Up Questions—Maze AI makes uncovering in-depth insights simple.
2. Closed card sorting
Unlike open or hybrid card sorting, closed card sorting uses predefined categories to evaluate specific usability issues in an existing design.
By analyzing how participants group and categorize information, researchers can identify potential issues, inconsistencies, or gaps in the design's information architecture, leading to improved navigation and findability. The results offer quantitative insights into users' mental models and expectations.
Closed card sorting allows researchers to:
- Understand how users categorize information
- Identify mismatches between user expectations and the existing structure
- Improve the overall user experience by ensuring that navigation aligns with user logic and behaviors
Consider asking these questions when conducting closed card sorting:
- Which categories were you unsure about?
- Why were you unsure about the [X] category?
- Did you consider placing [X] card in any other category?
3. Tree testing
Tree testing, also known as reverse card sorting, is a research method used to evaluate the findability and effectiveness of information architecture. Participants are given a text-based representation of the website's navigation structure (without visual design elements) and are asked to locate specific items or perform specific tasks by navigating through the tree structure. This method helps identify potential issues such as confusing labels, unclear hierarchy, or navigation paths that hinder users' ability to find information.
When comparing tree testing vs. card sorting:
- Tree testing evaluates the effectiveness of a site's navigation by having users find specific items in a text-based hierarchy
- Card sorting involves organizing information into categories to reveal users' mental models and improve information architecture.

Tree testing allows researchers to:
- Evaluate the clarity and effectiveness of category labels
- Identify problematic navigation paths and areas of user confusion
- Optimize information architecture to improve user findability and task completion rates
Consider asking these questions during or after a tree testing session:
- How confident were you in the path you chose?
- Were there any labels or categories that confused you?
- Did you expect to find [X item] in a different category?
- How would you rename any labels to make them clearer?
- At any point, did you feel lost or unsure about where to go next?
4. Usability testing
Usability testing involves observing and collecting qualitative and/or quantitative data on how users interact with a design or product. Participants are given specific tasks to perform while their interactions, feedback, and difficulties are recorded. This approach helps identify usability issues, areas of confusion, or pain points in the user experience.
There are different types of usability testing, including:
- Guerilla testing: Quick and inexpensive, conducted in public places to gather immediate feedback from random users
- Five-second test: Participants are shown a design for five seconds and then asked questions to capture their first impressions
- First click testing: Evaluates the effectiveness of the first click a user makes to complete a task, crucial for understanding navigation efficiency
- Session replay: Records and replays user sessions to analyze behavior and interactions with the design
Some usability questions to consider include:
- How would you go about performing [task]?
- How was your experience completing [task]?
- How was your experience when navigating to [X] page?
- Based on the previous task, how would you prefer to do this action instead?
💡 Recruiting participants for UX research can be tough
With the Maze Panel, you can quickly and easily recruit research participants who meet your criteria, from a pool of over 3 million participants.
5. A/B testing
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is an evaluative research approach that involves comparing two or more versions of a design or feature to determine which one performs better in achieving a specific objective. Users are randomly assigned to different variants, and their interactions, behavior, or conversion rates are measured and analyzed. A/B testing allows researchers to make data-driven decisions by quantitatively assessing the impact of design changes on user behavior, engagement, or conversion metrics.
This is the value of having a UX research plan before diving into the research approach itself. If we were able to answer the evaluative questions we had, in addition to figuring out if our hypotheses were valid (or not), I’d count that as a successful evaluation study. Ultimately, research is about learning in order to make more informed decisions—if we learned, we were successful.
Nannearl LeKesia Brown
UX Researcher at Figma
Ask questions like these to understand the why behind user behavior in A/B testing:
- Which version felt more intuitive to use, and why?
- Which version helped you complete the task faster or more easily?
- Was there anything in [Version A/B] that confused or distracted you?
- If you had to choose one version, which would you prefer—and what makes it better?
3 Evaluative research examples and case studies
Across UX design, research, and product testing, evaluative research can take several forms. Here are three examples of evaluative research:
Comparative usability testing
This way to conduct evaluative research involves conducting usability tests with participants to compare the performance and user satisfaction of two or more competing design variations or prototypes.
You’ll gather qualitative and quantitative data on usability metrics like task completion rates, errors, user preferences, and feedback to identify the most effective design option. You can then use the insights from comparative usability testing to inform design decisions and prioritize improvements based on user-centered feedback.
Cognitive walkthroughs
Cognitive walkthroughs assess the usability and effectiveness of a design from a user's perspective.
You’ll create evaluators to identify potential points of confusion, decision-making challenges, or errors. You can then gather insights on user expectations, mental models, and information processing to improve the clarity and intuitiveness of the design.
Diary studies
Conducting diary studies gives you insights into users' experiences and behaviors over an extended period of time.
You provide participants with diaries or digital tools to record their interactions, thoughts, frustrations, and successes related to a product or service. You can then analyze the collected data to identify usage patterns, uncover pain points, and understand the factors influencing the user experience.
Wrapping up
In the next chapters, we'll learn more about quantitative and qualitative research, as well as the most common UX research methods. We’ll also share some practical applications of how UX researchers use these methods to conduct effective research.
Frequently asked questions
What is evaluative research?
What is evaluative research?
Evaluative research, also known as evaluation research or program evaluation, is a type of UX research used to evaluate a product or concept and collect data that helps improve your solution.
What are the goals of evaluative research?
What are the goals of evaluative research?
Evaluative research assesses the effectiveness, identifies improvement areas, and measures user satisfaction. It checks if a design achieves its objectives, enhances user experiences, and offers insights for future enhancements.
What is evaluative research design?
What is evaluative research design?
Evaluative research design is a structured approach to planning and conducting UX research to assess the usability and impact of a product. It includes formative evaluation to test and refine designs during development, summative evaluation to assess the final product's overall effectiveness, and outcome evaluation to measure long-term impacts on user behavior and satisfaction.
Is evaluative research the same as evaluative research design?
Is evaluative research the same as evaluative research design?
Evaluative research is often conflated with evaluative research design, but they’re not the same. The key difference between the two lies in their scope and focus.
- Evaluative research focuses on assessing the usability, effectiveness, and performance of a product. Common methods used in evaluative research include usability testing, UX surveys, A/B testing, tree testing, and heuristic evaluations.
- Evaluative research design is a strategic framework that guides how evaluative research is conducted. Evaluative research design is used in various fields, including education, social sciences, and healthcare.
What is the difference between evaluative and formative research?
What is the difference between evaluative and formative research?
Evaluative research measures the success of a completed design, focusing on outcomes and user satisfaction. Formative research occurs during development, identifying issues and guiding iterative adjustments to meet user needs.