Without data, decisions about which new product ideas to pursue are mostly guesswork. In the early stages of product development, effective idea screening allows you to avoid wasting time and resources on ideas that are unrealistic or that don't meet your business objectives and target audience’s expectations.
If you're looking to implement effective idea screening processes and make confident product decisions, this step-by-step guide is for you. Look out for tips and insights from researchers to guide you along the way, plus a list of key questions to ask during idea screening.
What is idea screening?
Idea screening is the process of evaluating product ideas to determine which are worth pursuing. It typically happens at the early stages of the new product development process and is followed by concept testing.
During idea screening, researchers consider specific criteria such as market potential, technical feasibility, and strategic fit to identify the ideas that best align with company objectives and user needs.
As Matthieu Dixte, Product Researcher at Maze, describes, “Idea screening presents a good opportunity to analyze how people understand your idea. What benefit do we see in these ideas? What's working or not?” The goal is to filter out product ideas and determine which ones are most likely to be successful.
What's the difference between idea screening and concept validation?
It’s important to understand the difference between idea screening and concept validation. Idea screening happens earlier in the new product development process to identify the ideas with the highest chance of success.
Concept development and validation only happens once you've narrowed down your initial ideas and are ready to speak to users and determine market potential before investing time and resources into development.
4 Benefits of screening ideas before building a new product
As UX Researcher Lade Tawak says, “Idea screening brings you back to your business objectives.” When you start with this approach, it becomes much easier to align yourself with your target market and minimize the risks associated with new product development.
In particular, idea screening can help you:
Minimize risks and project failure
When you conduct product research and evaluate ideas from the early stages of product development, you avoid losing time further down the line when unforeseen challenges arise. For example, during idea screening for a new SaaS product, you might realize that getting the necessary certifications and regulatory approvals would be too time-consuming and costly. With that information, you can make an informed decision about the feasibility of the idea.
Optimize resource allocation
By allocating resources exclusively to your most promising ideas, you can maximize your chances of increasing your ROI. This optimization allows you to spend time and energy on the right concepts so you can preserve your team's ability to focus and innovate.
Reduce subjective biases
With measurable evaluation criteria and a systematic approach to idea screening, you can minimize the influence of personal preferences or cognitive biases. This ensures that every idea gets assessed in a transparent and consistent way. For example, with criteria such as market potential, technical feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and alignment with company goals, you'll get a fairer, more realistic view of which of your ideas is best.
Gain a competitive advantage
Evaluate your product ideas to identify unique features, market opportunities, or competitive advantages that'll set your product apart. You can follow this up with concept testing through research methods like surveys and customer interviews to validate your solution with real user insights and plan the next steps.
Explore real-life examples ✨
See how successful companies keep innovating and delivering increased customer value with these seven new product development examples and strategies.
Your step-by-step guide to the idea screening process
Idea screening helps you focus your efforts on projects that are more likely to succeed. Here's how you can set up your idea screening processes to get accurate insights into what your customers need.
1. Host an idea generation session
You can use idea screening for brand new products, individual features, and updates on existing products. To ensure all possibilities have been explored, you need to generate a high number of ideas before narrowing down and selecting the best ones. This involves bringing together your team and stakeholders for idea generation or product discovery brainstorming.
To host a productive session, you should:
- Ask practical questions such as "What problem are we trying to solve?" and "What customer needs are we filling?"
- Encourage free discussion and creativity by using brainstorming techniques such as storyboarding and mind-mapping
- Group similar ideas together so you can notice trends and find areas where you need to conduct further research
This process will bring different perspectives from your team, which will help reduce biases and address potential user issues even before putting the ideas to the test. For example, a product manager might think of a new feature requiring high internet speed. Yet, you might flag that your users are mostly from countries with low internet speed, so they wouldn't be able to use that feature.
2. Establish your screening criteria
It's a good idea to decide on an objective set of criteria to assess the worth of your ideas, and make sure they meet your business goals. This step will give your screening process a north star to aim for—and keep you from falling off course.
Examples of screening criteria include:
- Market saturation: Consider how many competitors your idea would have in the target market, and weigh up what the demand would be for your new solution
- Audience impact: Analyze how many ways your target audience could benefit from your new product as well as how many people it could help
- Brand fit: Ensure that your new idea reflects your brand's positioning and resonates with your existing customer base
- Feasibility: Determine whether the proposed solution is viable for your business considering available tools, expertise, and resources
- Return on investment: Calculate how much money you'll need to invest—including costs related to research and development, marketing, distribution, and ongoing support—and how much you expect to get in return
- Scalability: Assess the ability of your new idea or product to accommodate increased demand, expand to new markets or customer segments, and adapt to evolving customer needs and technologies
You can also determine the weight of each criterion in decision-making. Let's say one of your business goals is to serve enterprises. If your idea has a high projected ROI and technical feasibility but isn't scalable, you might need to rethink or discard it because it's not serving high-level goals.
3. Conduct a preliminary screen with qualitative research
Building out the "why" behind your new product idea is vital as this will form the guiding principles for your decisions going forward. An example might go like this:
“What if we allow people to checkout without having an account?”
“Why?”
"Because during feedback sessions, users complained about having to log in or sign up to purchase, and competitors like X and Y don't have this step."
Leverage qualitative research methods that give you deeper insights into your users' pain points and desires to evaluate your ideas. Methods can include:
- Focus groups: Get a more holistic assessment of your ideas' strengths, weaknesses, and alignment with organizational goals by bringing diverse perspectives together
- Surveys: Identify one or two areas of evaluation and run a survey to gather user feedback at scale. Keep in mind these survey design principles to ensure you keep participants engaged.
- User reviews: Validate ideas about customer needs by looking at your own or your competitors' reviews, and keep an eye out for any patterns or comments that stand out.
For example, use focus groups to observe and listen to how people talk about your product, what users believe are the most important features, and what problems they experience. Send surveys to respondents to dig deeper into comments or user feedback from sales churn calls or customer support tickets. Lastly, read user reviews to prevent making the same mistakes as your competitors or conduct further research on the performance and usability of certain features.
4. Get granular with quantitative research
Quantitative research provides the hard data to back up your qualitative research insights. For example, compile information about competitor pricing, sales and investments, and market growth rate.
Try creating a spreadsheet for recording competitor information. To keep it easy to digest, add a summary table similar to this one:
| Main competitors | Basic plan price (per user per month) | Enterprise plan price (per 100 users per month) | Annual published revenue | Market share growth (vs. year ago) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Competitor 1 | $8.99 | $850 | $1,967,900 | 27% |
|
Competitor 2 |
$7.58 | $700 | $2,983,988 | 15% |
|
Competitor 3 |
$9.99 | $900 | $2,778,666 | 17% |
You can compare these metrics to previous tests and competitor insights. For example, if you hear in sales calls that Competitor 1 simplified its onboarding process, you might guess it was successful because it grew 27% in a year. You can also assess these competitors' net promoter scores (NPS).
For an even broader analysis, invite everyone on the product, marketing, sales, or customer support teams to add their insights. As Lade Tawak highlights, it's a good idea to "get everyone together to have a two-minute call to share insights from the data points." That's because each team might find different valuable insights and can leverage them in their roadmap decisions.
Tip ✨
One common product discovery mistake is leaving engineers or other departments out of the process. Learn how to design cross-functional teams for research and how to overcome product discovery mistakes.
5. Prioritize and assess the feasibility of your ideas
After you collect all the previous data and get a list of the most promising ideas, you should conduct a more in-depth analysis to assess feasibility. Invite other teams to understand if you have the technology to develop your solution and the capacity to handle the impact of these changes.
For example, let’s say you simplify the signup flow, and along with SEO initiatives bringing more traffic, you end up getting 20% more signups in a month. Can your website support 20% more active users? Can your support team handle 20% more inquiries on time?
After defining feasibility, you'll need to rank the remaining ideas based on alignment with the screening criteria, market potential, and scalability.
6. Begin concept testing
Now that you've narrowed down your key ideas, it's time to look at specific concepts and solutions. To properly validate your concepts and ideas, you'll need feedback from your target customers. Concept testing can involve:
- Using simulations, animations, and sketches to make it easier for your audience to visualize your idea
- Conducting concept testing surveys where you can ask questions like "What are your favorite aspects of Concept A?"
- Running customer interviews or focus groups to gather qualitative information and more in-depth insights
- Using comparative testing (not to be confused with A/B testing) to get your audience's insights on two or more concepts
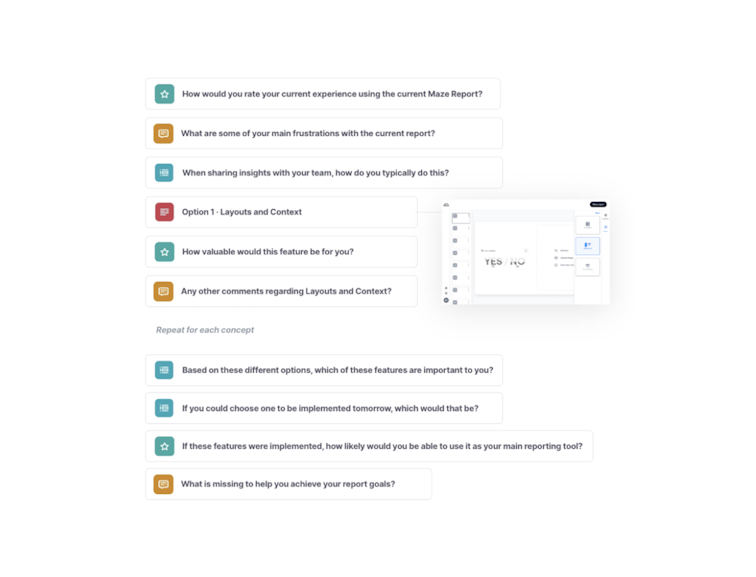
Questions to ask to validate your idea during concept testing
Product tip ✨
Use Maze to accelerate your concept testing processes with both quantitative and qualitative data. Get quick user reactions with five-second tests, mine actionable data with open questions, and test prototypes directly—all in the same, easy-to-use platform.
What questions should you ask during idea screening?
To stay aligned with your target audience and company goals, here's some questions you should consider when idea screening:
- What is the business goal? Focusing on the deeper mission behind your product ideation helps you ensure a coherent product roadmap and identify ideas that contribute toward it.
- Which real user issues will the idea solve? In Lade's words, "If your idea doesn't benefit your customer database, there's no business value in it." For that reason, you should avoid making any assumptions about your target audience and truly understand their needs by adopting a continuous product discovery mindset.
- What is the size and growth forecast for the target market? Aligning your ideas with the market's trajectory helps accurately assess feasibility and make decisions about resource allocation.
- What are the risks/challenges associated with the idea? Lade also describes the importance of assessing the level of risk involved with an idea. "Do you already have enough insights to put something out there and see if it works? Or are you unsure of where you're starting?"
- Could later changes in the market impact the idea? By continually analyzing market and industry trends, emerging technologies, and customer preferences, you can assess the long-term viability of your ideas.
Scaling your business with idea screening & concept validation
Idea screening can save you precious time and resources and provide you with market insights that can set you apart from the competition. To create solid processes and obtain valuable data, you should follow these key steps:
- Host an idea generation session
- Evaluate your ideas against specific criteria
- Conduct qualitative and quantitative research
- Run concept testing
As you scale, validating your ideas and concepts with real users is crucial to staying aligned with your company objectives. With a continuous product discovery platform like Maze, you can bring your customer voice to the entire product development process. This enables you to adapt to changes in the market and meet customers' needs and expectations.
Frequently asked questions about idea screening
What is the idea screening process?
What is the idea screening process?
Idea screening is a stage of product development in which ideas are evaluated to determine which ones best align with company goals and target audience. To do so, testers will consider market potential, feasibility, and strategic fit criteria.
What’s the main purpose of idea screening?
What’s the main purpose of idea screening?
Idea screening allows you to save time and resources by avoiding pursuing ideas that aren't feasible or suitable for the target market. When done properly, it also gives you a competitive advantage by providing insights into your target audience.
What are the most important tools for idea screening and concept testing?
What are the most important tools for idea screening and concept testing?
To screen ideas and run concept testing, you need tools that give you quantitative and qualitative data. With Maze, for example, you can run five-second tests, surveys, and prototype tests and get actionable insights in hours.
What’s the difference between idea screening and idea generation?
What’s the difference between idea screening and idea generation?
Idea screening and idea generation are distinct stages in product development. Generation involves brainstorming to come up with a wide range of ideas, while screening is about evaluating and analyzing these ideas to select the most promising ones.
What’s the difference between idea screening and concept validation?
What’s the difference between idea screening and concept validation?
The difference between idea screening and concept validation is that idea screening occurs at the early stages of product development and involves evaluating a large number of ideas to identify the most promising ones for further exploration.
On the other hand, concept validation takes place after idea screening to evaluate the feasibility, appeal, and potential success of the chosen concepts and ideas before they're built.