When you need user research support quickly and cheaply, artificial intelligence can be a huge time-saver. However, while generative AI models like ChatGPT speed up user research, they can often provide lackluster responses.
But the problem isn’t the tool itself—it’s how you use it that counts.
Crafting actionable, specific, and contextual prompts makes all the difference, helping you streamline UX research and squeeze the most value from LLMs.
In this article, we show you how to craft effective AI prompts for user research, along with examples, challenges, and how to overcome them with the help of Maze.
TL;DR on AI prompts for user research:
- AI can speed up user research, but you need good AI prompts to ensure accurate output
- You can use techniques like the REFINE, CARE, and RACEF frameworks to guide your prompt writing
- Start by explaining your role and your objective
- Outline the format and structure you want the response given in
- Provide any specific details or nuanced context
- Don’t accept the first answer: go back and forth to iterate on AI’s response until it meets your needs
- Always ask AI tools to cite their sources and give references—then check these!
- Watch for biased or leading questions within your prompts
- Tools like Maze can help detect bias and re-phrase questions for you
Best practices for crafting AI prompts: 3 Frameworks to guide prompt writing
Great questions lead to great answers—it’s a maxim that holds true for both people and bots. By structuring your AI prompts with specific steps, you can ensure relevant (and usable) responses for every question.
As Andrea Monti Solza, Researcher & Co-founder of AI-powered platform Conveyo, puts it:
“AI has given us the opportunity to do research faster. There is power in that. But we also know, because of how imprecise and context-unaware AI is, that it works better in the hands of an expert.”
Knowing how to ask the right question—or rather give the right prompt—can be tricky. Luckily, just like for UX design, frameworks exist to help you get the best out of artificial intelligence when it comes to crafting your prompts. Let’s go through them.
If you’re good at prompting, you can get information very quickly. But you still need the right oversight.
Andrea Monti Solza
Researcher & Co-founder of Conveyo
Share
The REFINE framework

The REFINE framework is a prompting strategy based on the Double Diamond method—a UX framework to guide teams from problem identification to solution delivery.
REFINE stands for:
- Role
- Expectation
- Format
- Iterate
- Nuance
- Example
This framework makes it easy to generate helpful responses for complex topics, ranging from research plans to in-depth interviews, then drill down into the details and work out a highly precise answer.
The REFINE framework is divided into two phases:
- Exploring options: Getting AI to generate a number of options and ideas for you
- Specific details: Narrowing down and iterating those ideas until you have your final output
Both phases pull from the sections about (role, expectation, format, iterate, nuance, example) to structure your prompt and ensure the AI tool has adequate input and guidance.
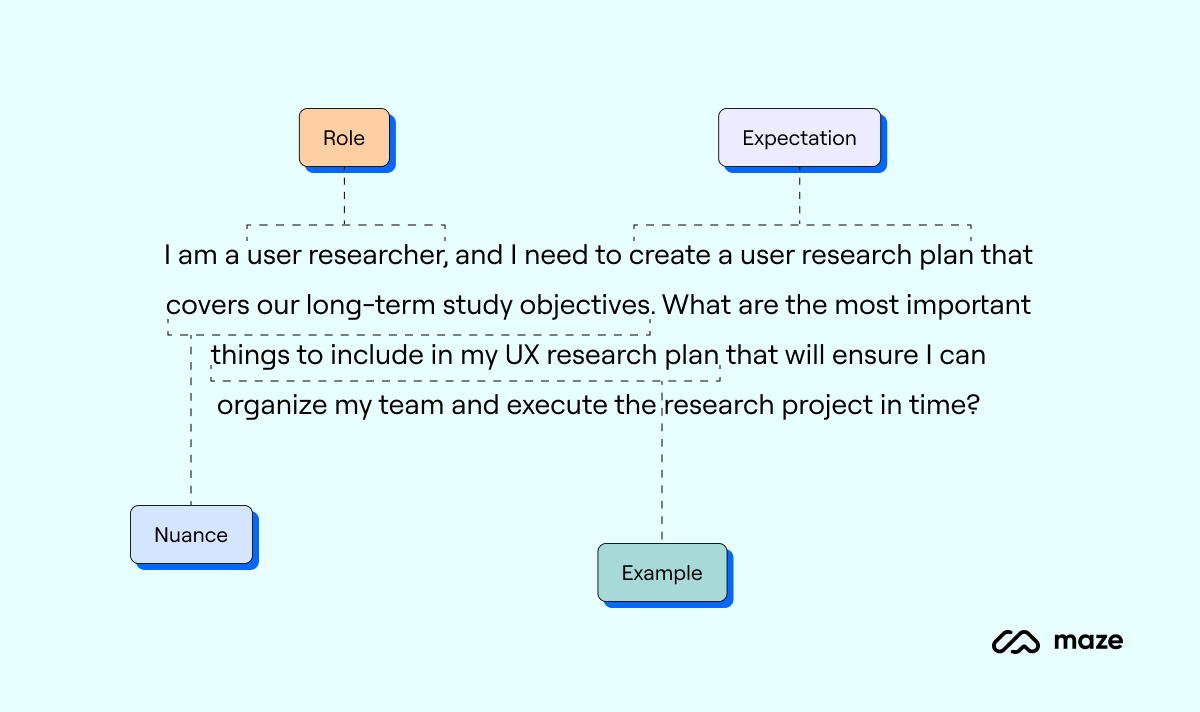
Let’s say you need to create a UX research plan. Starting by exploring options, here’s how the first part of your prompt using the REFINE framework might look:
- Role: User researcher
- Expectation: User research plan
- Nuance: Covers long-term study objectives
- Example: What should be included in the plan
So your prompt might be:
Say you’re using ChatGPT, the response might look something like:
To create a user research plan covering long-term study objectives, you should include the following in a UX research plan:
- Research Objectives: Define what you want to learn in plain language. This keeps the team focused on business and user goals, not just methods.
- Methodology & Study Design: Detail which methods you'll use (e.g., interviews, diary studies, surveys, usability tests), and when in the timeline.
- Timeline & Milestones: Lay out a timeline with major activities, fieldwork, analysis, stakeholder check-ins, deadlines, and deliverables.
Including these elements in your UX research plan will ensure your team can organize and execute the research project in time.
Now you’ve got the first part of your answer, but it doesn’t end here. The first response you get won’t be the answer you accept.
Moving onto the specific details phase, your reply prompt can be guided by the REFINE framework to include:
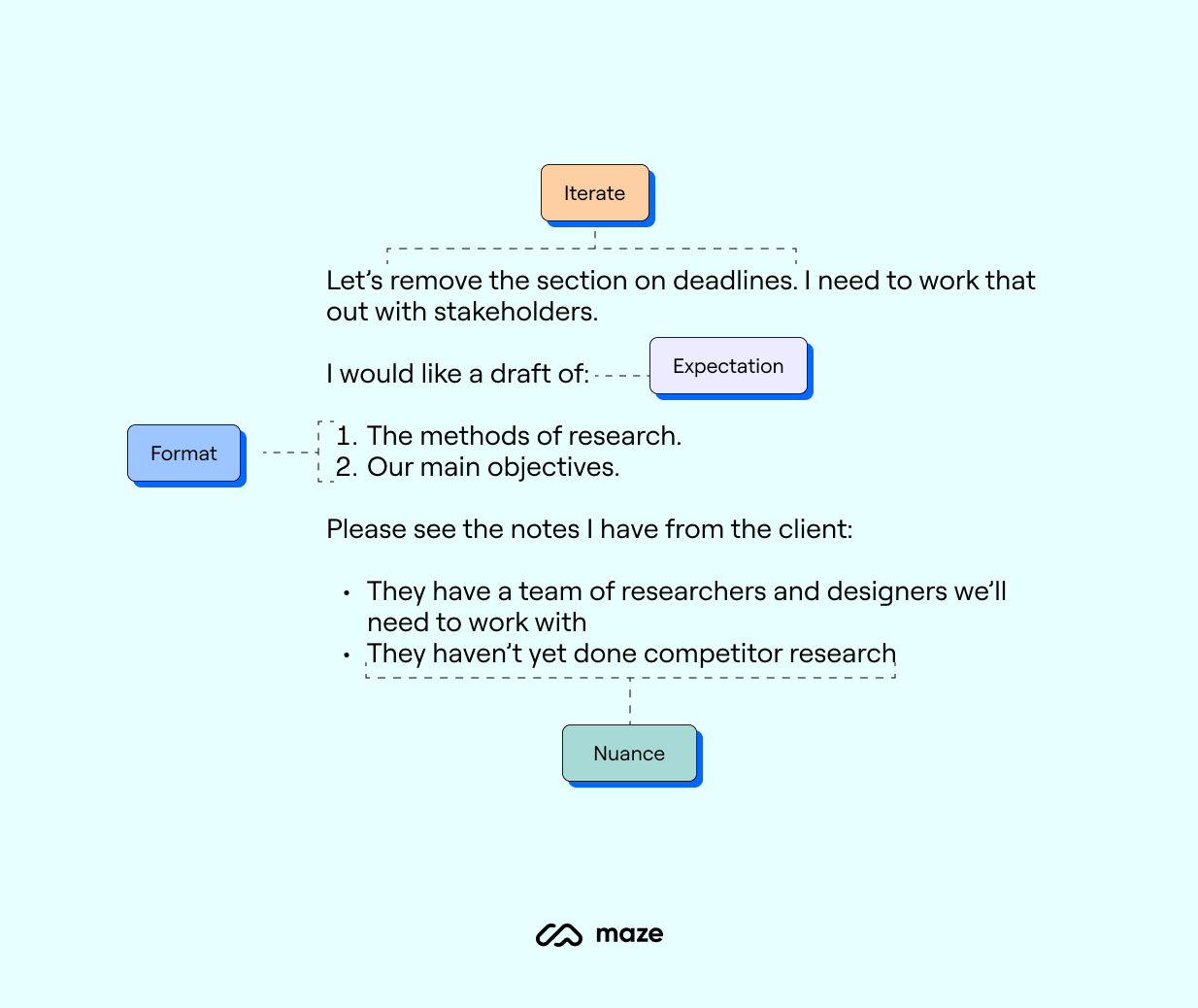
- Iterate: Remove any unnecessary sections, specify additions needed
- Expectation: Outline a draft is needed
- Format: Specify the format required
- Nuance: Factor in any specific notes or context
Your next prompt might be:
Finally, your AI should give you a more specific answer, like:
Of course, here is a revised UX research plan considering long-term objectives and the notes from your client. I have outlined main objectives and key methods of research.
Core Long-Term Objectives:
- Validate core user problems & Jobs-to-Be-Done
- Benchmark the competitive landscape (fill current gap)
- Track UX quality over time with baseline metrics
- Surface unmet or emerging user needs to feed future roadmap bets
- Keep researchers, designers, and PMs aligned on actionable insight
Essential Research Methods (lean list):
- Stakeholder interviews: Capture internal assumptions and success criteria
- Contextual inquiries/field visits: Observe real workflows and constraints in situ
- Diary studies + jobs-to-be-done interviews: Uncover motivations, triggers, and longitudinal pain points
- Competitive teardown & heuristic audit: Analyze top competitor features, flows, and UX quality
- Quantitative satisfaction survey: Validate which experience factors drive or erode loyalty at scale
The REFINE framework is a great way to dig into a prompt and iterate on the answer AI gives you. By mixing-and-matching which elements of REFINE you need to specify at what time, you can ask a more specific prompt and gather a deeper answer.
The CARE framework
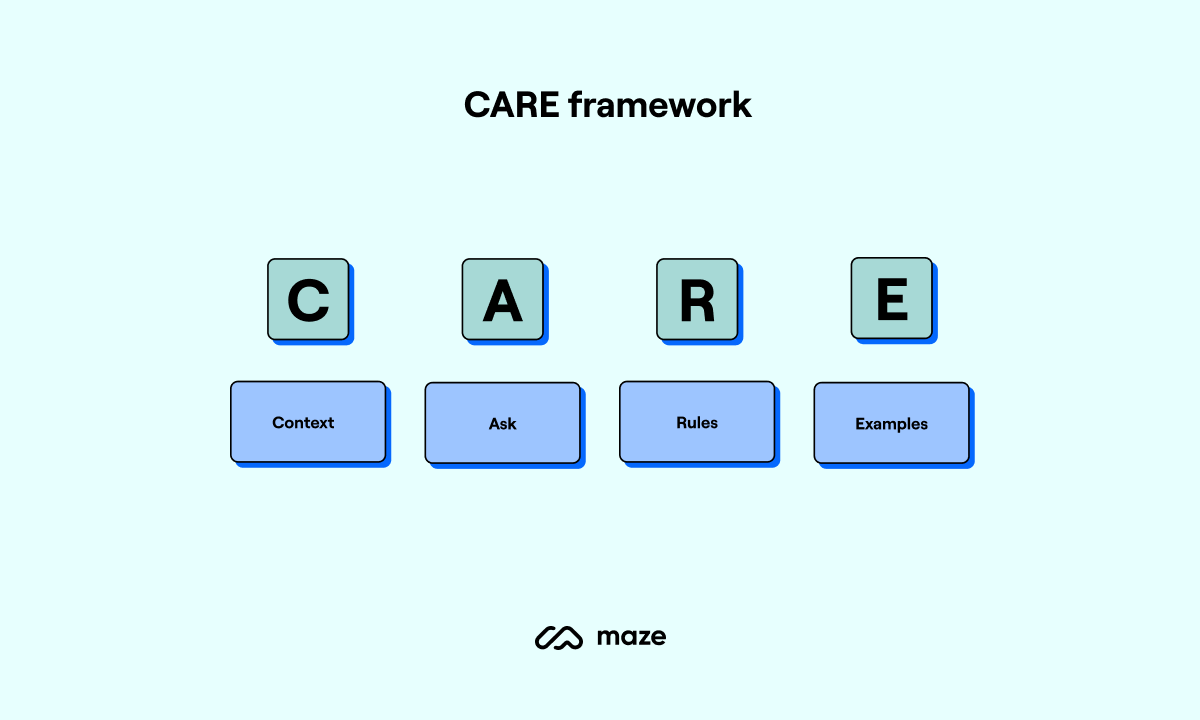
The CARE framework is a prompting approach that organizes your AI input into:
- Context: Describe the situation
- Ask: A specific question
- Rules: Provide constraints
- Examples: Demonstrate what you want
CARE is especially useful for getting in-depth, multi-faceted responses to complex problems.
Here’s an example prompt:
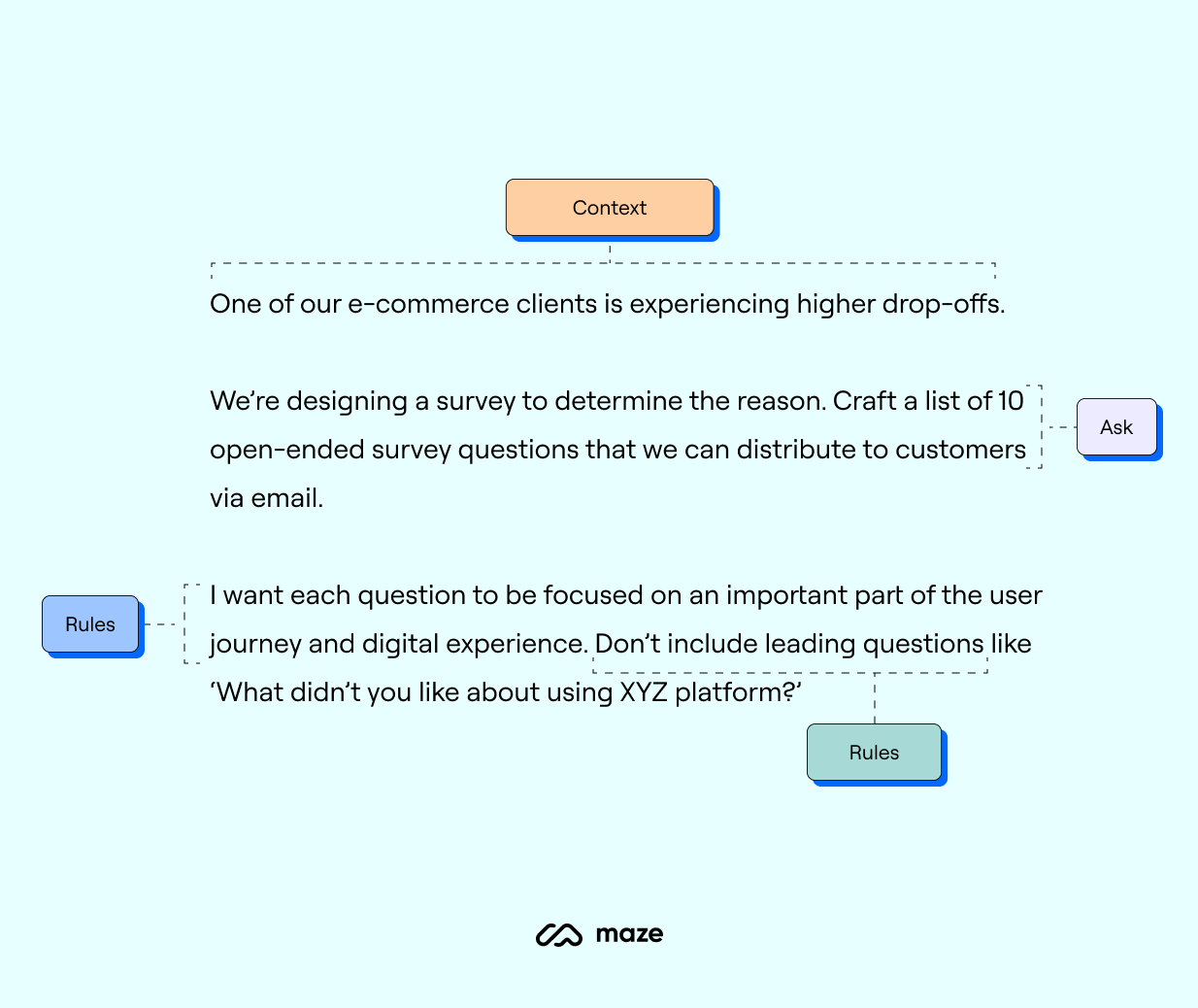
In this example, you deliver context about your client, the problem, and objective. You ask for specific survey questions, with the rules around question focus, and give examples for what you don’t want (this also counts somewhat as a rule).
AI’s answer to this prompt might be:
Happy to help! Here is a list of 10 non-leading open-ended survey questions you can deliver via email to your e-commerce client to determine the reason behind their higher drop-off rate.
- When you first arrived on our site, what impressions or thoughts came to mind, and how did they shape what you did next?
- Can you walk us through how you usually look for a product when you shop online and how that experience felt on our site?
- Tell us about the factors that help you decide whether a product page gives you enough confidence to keep moving toward purchase.
- How did the information, images, or reviews you encountered influence your feelings about the product you were considering?
- Describe any moments while browsing our catalog when you paused, hesitated, or needed extra clarity before continuing.
- Thinking about adding items to your cart, what details or prompts make that action feel worthwhile to you?
- Please share your experience navigating the cart—what you noticed, considered, or needed before choosing to proceed to checkout.
- As you moved through the checkout steps, what aspects of the process stood out and affected your willingness to complete the purchase?
- Reflecting on payment and delivery options, what qualities or information matter most to you in feeling confident to finalize an order?
- After leaving our site, what additional thoughts or needs emerged that could influence whether you return and complete a purchase later?
The RACEF framework
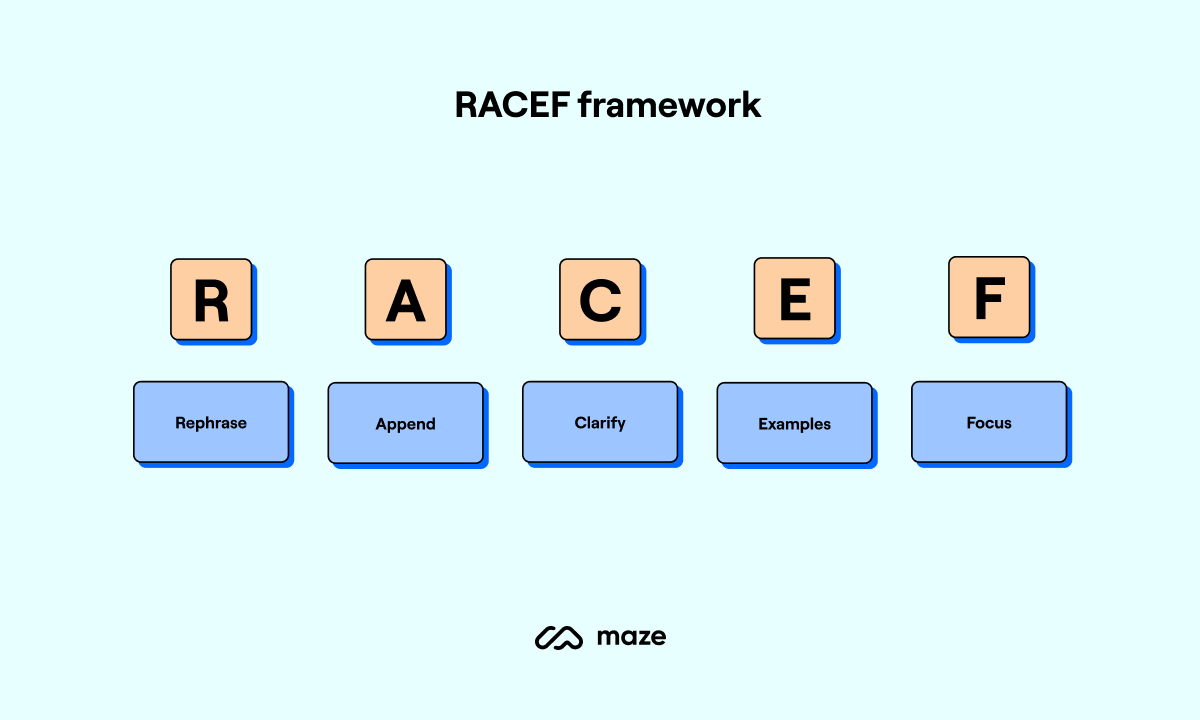
RACEF is a framework that offers a structured and highly versatile approach to prompting. It stands for:
- Rephrase: Refine questions for optimal clarity
- Append: Enrich prompts with details and constraints
- Clarify: Encourage iterative improvement
- Examples: Demonstrate formats
- Focus: Narrow the scope for accuracy
The RACEF framework is ideal for exploratory, nuanced tasks that require large amounts of detail before refinement.
For example, image you’ve given the LLM a user interview transcript and want it to analyze the interviews. Here’s what an example prompt would look like:
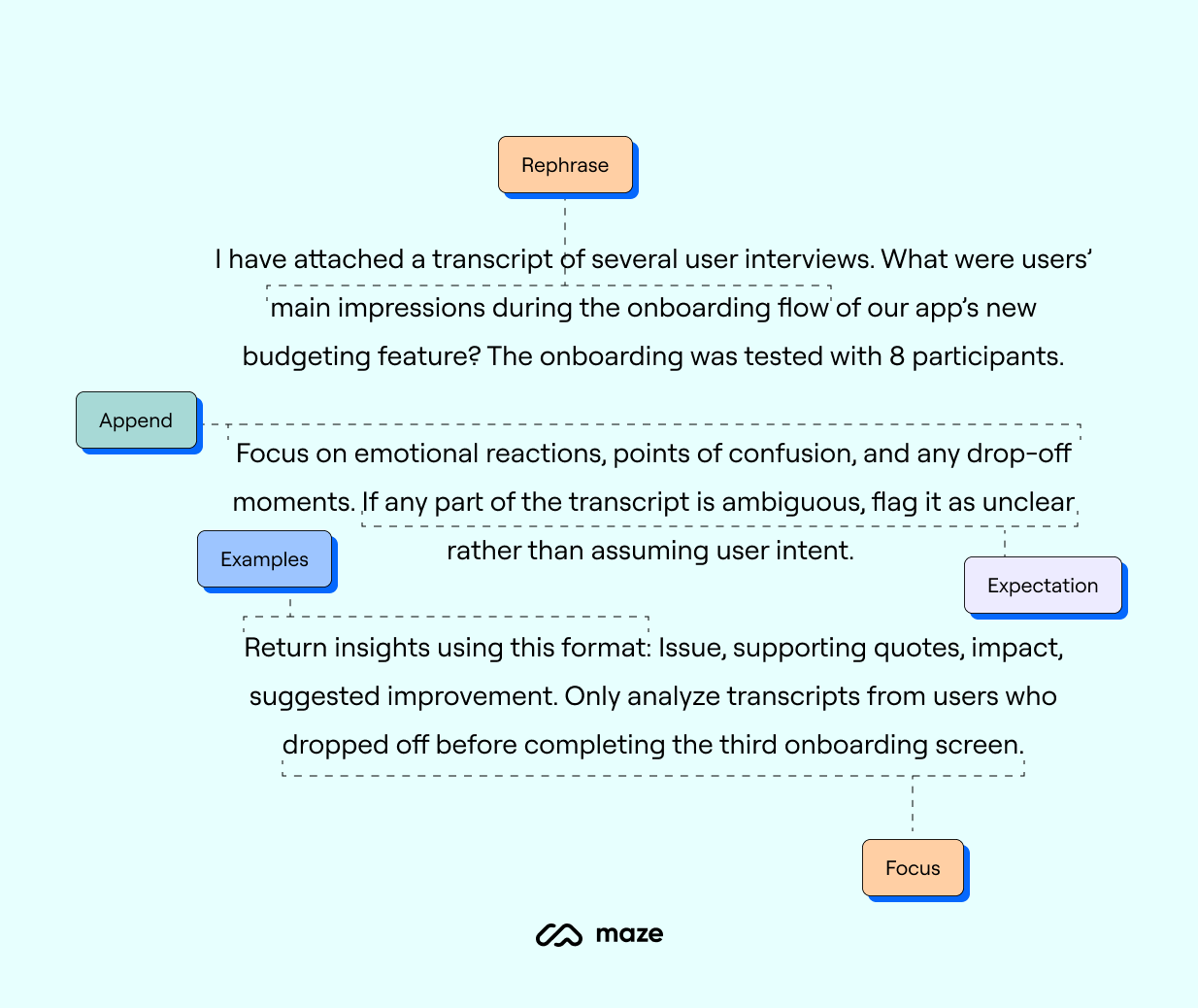
Following the RACEF framework, you’ve outlined what you’re looking to learn, the context and focus, given clear instructions and examples. Ultimately leading you to a productive AI answer!
Example AI prompts for user research by use case
The above frameworks provide structure to your prompting so you can make the most of AI in your UX research process.
However, if you’d prefer to dive straight in, here are some plug-and-play AI research prompts that you can run with straight away.
AI prompts for interview preparation
From thinking up open-ended interview questions to assembling a UX research discussion guide, user interviews are notorious for lots of prep work.
To make the process easier, here are five AI prompts you can customize and refine to your need, or use immediately as-is.
1. Draft a [X]-minute semi-structured interview guide for power users who churned from our [product] within the last [time period]. Include seven core questions, two follow-up questions each, plus an ice-breaker at the beginning and a wrap-up at the end. Focus the core questions on feature gaps and emotional triggers of churn.
2. Convert these research goals into concrete, non-leading interview questions for remote participants, adding one plain-language probe per goal. Flag any goal that still lacks enough context. Here are the five research goals: [insert research goals]
3. Draft a [X]-minute discussion guide to explore users’ first impressions of our [product]. Break it into five timed sections (intro, context, tasks, reflection, close) and add two probing follow-ups per section to uncover emotions and unmet user needs.
4. Check the following interview questions for any bias, leading questions, or irrelevance. If you find any, provide a new list of objective questions. [insert interview questions]
5. Generate a comprehensive pre- and post-checklist for moderators running UX interviews. Include important elements like tech setup, rapport-building reminders, and note-taking cues.
AI prompts for survey design
Designing user surveys can be time-consuming, especially when it comes to writing a mix of closed-ended, open-ended, multiple-choice, and Likert scale questions.
While AI won’t necessarily get you a perfect question from the first response, it’s great to provide a base design idea for your survey questions that you can iterate on.
1. Write a 12-question survey to measure the appeal of our feature among [demographic] users who logged in this month. Use 5-point Likert, open-ended, and closed-ended questions.
2. Turn the hypotheses below into survey questions, ensuring each item is unbiased and single-focused. Provide the recommended response format and a one-line rationale for every question. [insert hypothesis]
3. Rewrite the draft survey I’m pasting to keep completion time under [X] minutes. Replace any leading questions with neutral alternatives and mark your changes.
4. Create a 6-question screener survey to recruit project managers with at least [X] years of experience within the industry.
5. Design an 8-question pulse survey to gauge user satisfaction with our recently launched [feature] across web and mobile. Mix six 5-point Likert items covering [topic] with one NPS question. Keep completion time under [X] minutes.
AI prompts for data analysis
User research analysis is what turns your unrefined data into actionable insights. Manually analyzing the data requires:
- Using spreadsheets to calculate statistical insights for quantitative studies, like surveys
- Extracting overarching themes via thematic analysis from qualitative data like interview transcripts, prototypes, or wireframe testing
While there are many techniques for using AI to speed up analysis, such as AI thematic analysis, one way to speed up analysis is by feeding AI models prompts featuring key data points.
This technique can drastically reduce the time it takes to turn raw data into valuable insights—especially when dealing with large datasets. Here's some prompts to use:
1. Cluster the 200 open-ended NPS comments below into themes, label each theme, list two representative quotes, and report what percentage of comments each theme captures.
2. Analyze the attached CSV of in-app events to find the top three drop-off steps in the sign-up funnel over the last 30 days. Return a table with step name, drop-off rate, week-over-week change, and a 150-word insight summary.
3. Synthesize insights from these semi-structured interviews about our [product]’s [feature/functionality] tools. Code each quote by theme and sentiment, then deliver a ranked top-seven issues list with illustrative quotes and a ~100-word opportunity summary.
4. Process the attached Excel file of closed-ended survey responses on [subject]. Conduct user survey analysis: Calculate mean scores, top-box percentages, and any statistically significant differences across age groups, then output a concise results table.
5. Analyze 10-day diary entries from [respondent profile] using our [feature]. Surface recurring pain points and delight moments, plot them on a day-by-day journey timeline, and craft a narrative that spotlights context shifts and the biggest design opportunities.
5 Additional useful AI prompts for user research
From building convincing user personas to turning lengthy reports into stakeholder summaries—a UX researcher’s work is never done.
Here are five more prompts that can turn time-consuming tasks into a completed research to-do list.
1. Generate three concise personas for our [product] using the demographic and behavioral survey data attached. Each persona should be less than 150 words with motivations, pain points, and a memorable nickname.
2. Turn this [length]-word research report into a one-page executive summary with a headline, three key insights, and one recommended action per insight, written for C-level readers to get their buy-in.
3. Create an affinity-map legend that categorizes these sticky notes by user type, emotion, and task stage for our [research method] study. Define color codes, example note formats, and merging rules.
4. Draft five testable hypotheses in the format ‘We believe that ___ will improve ___ for ’ based on the friction points highlighted in the attached document.
5. Write a GDPR-compliant recruitment email inviting [profile] who use [software type] to join a [X]-minute remote interview next week. Include incentive details and a single-click Calendly link placeholder.
Challenges with AI use in user research
AI in UX research is very helpful, but it’s not perfect. And while plenty of UX researchers are seeing the benefits, there are also some pitfalls that come with machine learning algorithms.
Here are the three main challenges that often show up when using AI models, according to Andrea, Researcher & Co-founder of Conveyo.
Avoiding biased research questions
Cognitive biases in UX are one of the biggest challenges across all research, and AI-led research is no different.
Asking questions like “How easy was it to complete this task?” or “Would you agree the website is intuitive?” leads to inherently biased data and skewed insights.
Unfortunately, AI isn’t always objective and will occasionally provide leading or biased research information. This can depend on the data its fed, and also the training data it was built on.
When it comes to humans vs. AI user research, Andrea explains that humans need to think critically about AI outputs:
“The intelligence is handed over by humans based on what they taught the AI. The problem here is that if the training data is biased, as it tends to be, the answers will be too. AI is primarily a powerful processing tool—so it needs human oversight to catch the hallucinations and to correct bias.”
Ensuring inclusive research
A big part of effective UX research hinges on including diverse participants to reflect your complete user base.
A diverse group ensures your insights—and by extension, your product—is accessible, usable, and valuable. However, AI doesn’t always analyze data from diverse sets fairly.
AI can try to create the ‘perfect’ user, or provide you with the ‘correct’ answers—meaning the results lack nuance and diversity that is typically baked-in to human participants.
Training data is partly to blame for this challenge, due to homogenous data informing AI on what the ‘norm’ is.
What’s more, by processing data through AI multiple times, certain diverse perspectives or experiences can be filtered out by AI. Andrea cautions against over-iterating when data is in use, and being conscious to factor time for human oversight:
“Unless you guide AI, it will struggle to select the right, diverse audience. Even if you select the correct participants in an inclusive and diverse way, AI will tend to skew the data. You risk disregarding what makes those points of view unique because the more you iterate, the more the uniqueness is stripped out in order to make the feedback converge to a central bias.”
Data privacy and compliance with AI-driven research tools
Not all users will be comfortable with you processing their data through AI-powered research tools. Besides getting users’ consent, you’ll also need to keep them anonymous to prevent identification privacy violations and data breaches.
As such, it’s crucial to consider your legal responsibility and AI ethics in user research when handling data with AI tools. Andrea explains:
“Business should be about trust. Always tell people what you intend to do with the data. I would also be very clear about whether the use of data is going to be anonymous or not.”
Andrea also emphasizes to explain definitions and break down the specifics of how you will anonymize data for processing:
“Be clear about what ‘anonymous’ actually means—it's not just about name and surname. Is your location included? Is your background? Anything about your profession, your age, your medical records—whatever it might be.”
How Maze mitigates these issues
Despite these challenges, AI can be a hugely beneficial tool in your user research.
AI can be a really important tool in increasing and augmenting human capacity.
Geordie Graham
Senior Manager at User Research at Simplii Financial
Share
Just like AI is only as good as the prompts you give it, your AI research is only as effective as the AI tools you use.
With the help of Maze’s AI-powered features, you can mitigate concerns around biased data or privacy questions, and quickly ramp up your research production.
- Maze’s Perfect Question feature assesses your questions to check they’re bias-free and suggests alternatives.
- The dynamic AI Follow-Up tool helps you dig into insights in-the-moment, by generating contextual follow-up questions as users progress through your survey.
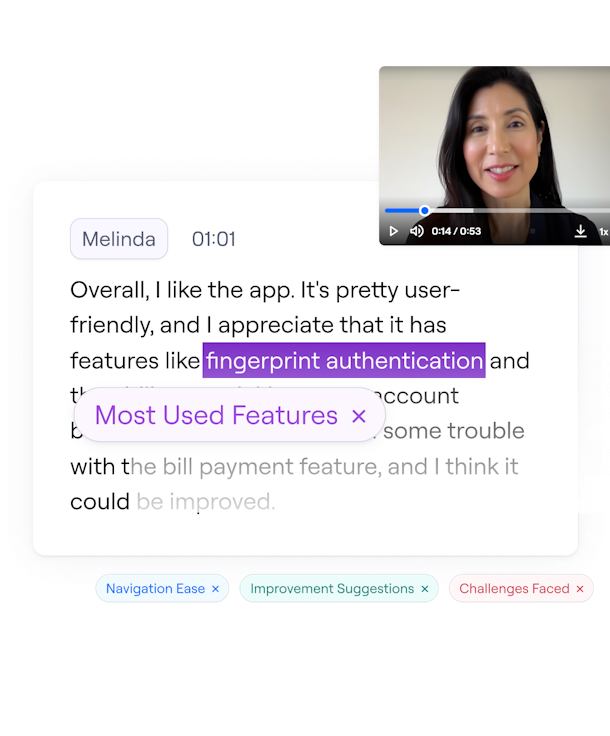
- Once your research is done, automatic analysis takes on the heavy lifting: digging into the data from Interview Studies and quantitative research to analyze user sentiment, identify key themes, and automate UX reporting.
From recruiting participants to turning data into actionable insights, Maze allows you to pick where and how you use AI, whether that’s as a co-pilot or an assistant. Either way, your research scales, and your time-to-insight decreases.
AI-powered tools to 10x your research
From recruitment to analysis, Maze AI makes going from question to insight faster than ever
Frequently asked questions about AI prompts for user research
How is AI used in user research?
How is AI used in user research?
You can use AI in user research to draft interview and survey questions, analyze UX research method results, and create a range of deliverables like user personas, recruitment invitation emails, plans for prototype testing and other UX research methods, and executive summaries.
Can AI do user research?
Can AI do user research?
AI like a companion, helping you streamline time-consuming tasks, brainstorm questions for your target audience, and automate analysis. It’s good at doing hyper-specific tasks, but professionals need to orchestrate the whole research and UX design process—ultimately developing a better user experience.
What are some good AI prompts for user research?
What are some good AI prompts for user research?
A good AI or ChatGPT prompt for user research is “Draft a structured interview guide for new users who have completed the onboarding experience in the last 20 days. Include seven open-ended questions that are objective, non-leading, and unbiased.”
Another great prompt: “Turn this 5-page research report into bullet points I can present to stakeholders. Extract context, key insights, and a recommended action per insight.”
What is an AI interview question generator?
What is an AI interview question generator?
An AI interview question generator creates interview questions for your user research based on the prompts you provide. They can be purpose-built or, more commonly, AI LLMs that you prompt to provide relevant interview questions.